Geothermal Energy: Earth's Natural Power Source
Imagine a world where the ground beneath us powers our lives. This world uses the Earth's heat, a natural and endless resource. It fuels our homes, businesses, and communities. This is the future of geothermal energy, changing how we use energy.
I've always been drawn to geothermal energy for its green and sustainable nature. The idea of using the Earth's heat for power is amazing. It shows our creativity and the Earth's strength.
We'll explore geothermal energy in depth. We'll look at its beginnings, how it's used, and its big impact on our energy use. Get ready to see the power and promise of this natural resource. It's a step towards a greener future.
Key Takeaways
- Geothermal energy is a renewable resource that taps into the Earth's internal heat to generate power and provide heating/cooling solutions.
- Geothermal power plants have a high-capacity factor, allowing for nearly continuous operation and 24/7 availability.
- Geothermal energy can contribute significantly to the U.S. electricity generation while using minimal water resources.
- Geothermal heat pumps can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to the annual emissions of 20 million cars.
- Geothermal energy is a clean source, with minimal emissions during electricity generation.

Introduction to Geothermal Energy
Definition and Origins
The word "geothermal" comes from Greek words "gê" (Earth) and "thermós" (hot). It refers to the heat from the Earth's core and crust. This heat comes from the Earth's formation and the decay of minerals deep down.
Historical Use and Development
People have used geothermal energy since Paleolithic times for bathing. The Romans used it for heating spaces. In 1827, the first industrial use was in Italy, extracting boric acid from volcanic mud.
The first commercial plant was built in Larderello, Italy, in 1911. In 1960, the first U.S. plant opened at The Geysers in California. Since then, geothermal energy has grown, with new uses and technologies.
Today, it's used for electricity, direct use, and geothermal heat pumps. This shows how far it has come.
" Geothermal energy is the heat within the Earth, generated by the Earth's formation and radioactive decay, that can be accessed for a wide variety of uses. "
Geothermal Resources and Potential
The Earth's internal heat is a huge source of geothermal energy. It comes from radioactive decay and the planet's formation. This natural heat is constantly renewed, making it a sustainable energy source.
Geothermal resources are most common near tectonic plate boundaries. These areas have thinner crusts and more heat flow. The "Ring of Fire" around the Pacific Ocean is a prime spot for geothermal energy because of its volcanoes and earthquakes.
Earth's Internal Heat and Tectonic Plate Boundaries
The Earth's core is incredibly hot, with temperatures over 4,000°C. This heat is a vast energy reserve. About 20% of this heat comes from the planet's formation, and the rest from radioactive decay.
A 2019 study found the U.S. could generate up to 60 gigawatts of electricity from geothermal by 2050. This could also lead to 17,000 district heating systems and 28 million geothermal heat pumps.
In 2022, another study showed the U.S. could reach 90 gigawatts of geothermal electricity by 2050. This would happen with faster and cheaper Enhanced Geothermal Systems. A report also suggested up to 300 gigawatts of next-generation geothermal power, thanks to new storage technologies.
Despite using only 0.7% of its geothermal resources, the U.S. is a leader in geothermal energy. It grows by 3% each year. With new technology, the U.S. is set to unlock more of its geothermal energy potential.
Types of Geothermal Energy Systems
Geothermal energy is a green and endless power source. It comes from the Earth's heat. There are three main ways to use this heat to make electricity.
Dry Steam Plants are the oldest and simplest. They use steam from underground to make electricity. The Geysers in northern California, USA, is the biggest dry steam field, with almost 1,500 megawatts (MW) of power.
Flash Steam Plants are the most common. They use hot, high-pressure geothermal fluid to make steam. This steam then makes electricity. The leftover liquid goes back into the Earth.
Binary Cycle Plants are more flexible. They use the heat from cooler geothermal resources. This makes it possible to use more places for geothermal energy.
The United States is the leader in geothermal power, with almost 4 gigawatts. This can power about 3 million homes. Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) could power over 40 million homes by 2050. By 2023, it could power over 65 million homes.
" Geothermal energy, a sustainable and renewable power source, can be harnessed through various types of energy systems. "
Geothermal Power Generation
Geothermal energy comes from the Earth's heat. It can be used to make electricity in different ways. These plants need hot water from deep inside the Earth to work well. There are three main types: dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle plants.
Dry Steam Plants
Dry steam plants are the oldest and simplest. They use steam from the Earth to make electricity. Only a few places in the world have these plants, like California and Wyoming.
Flash Steam Plants
Flash steam plants are the most common. They use hot, high-pressure water from deep in the Earth. When this water cools quickly, it turns into steam. This steam then powers turbines to make electricity.
Binary Cycle Plants
Binary cycle plants use a special fluid that boils at a lower temperature than water. This fluid gets hot from the Earth's water. Then, it turns into steam and powers turbines.
The right plant depends on the Earth's heat and water. New technologies like Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) are helping. They also use hot water from oil and gas wells.
| Geothermal Power Plant Type | Temperature Range | Efficiency | Greenhouse Gas Emissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Steam Plants | 300°F to 700°F | 7-10% | 45 g CO2/kWh |
| Flash Steam Plants | 360°F and higher | 7-10% | 45 g CO2/kWh |
| Binary Cycle Plants | 225°F to 360°F | 7-10% | 45 g CO2/kWh |
Direct Use and Heating Applications
Geothermal energy is more than just power. It can also heat buildings and power industrial processes. One great way to use it is through geothermal district heating systems.
These systems bring hot water from underground to buildings for warmth. They replace the need for many boilers, making heating more efficient and green. The oldest system in Chaudes-Aigues, France, has been working since the 15th century.
Geothermal energy is also used in food drying, gold mining, and pasteurizing milk. These uses don't need electricity, making geothermal even more efficient and sustainable.
| Geothermal Direct-Use Statistics | Value |
|---|---|
| Global Installed Geothermal Capacity (as of 2013) | 11,700 MW |
| Global Geothermal Electricity Production | 68 billion kWh |
| Geothermal Share of Electricity Production in Iceland and El Salvador | Over 25% |
| U.S. Geothermal Capacity | Over 3,300 MW |
| Geothermal Share of Electricity Production in California | Nearly 7% |
The use of geothermal energy and geothermal district heating systems shows its wide range of benefits. It can greatly help in making our energy use more sustainable.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps are a top choice for heating and cooling. They use the Earth's natural temperature. This makes them a green alternative to traditional systems.
How Geothermal Heat Pumps Work
These pumps use a fluid in underground pipes to move heat. In winter, they pull heat from the ground into buildings. In summer, they cool buildings by moving heat back into the ground.
Benefits of Geothermal Heat Pumps
- They save up to 60% on heating and cooling costs.
- They're eco-friendly, using no fossil fuels and making no direct emissions.
- They're quiet and need less upkeep than other systems.
- They last a long time, with parts lasting up to 24 years and the ground loop over 50 years.
- They can also provide hot water, making them versatile.
Choosing geothermal heat pumps is wise for those wanting to save energy and help the planet. As technology improves, more people are seeing the value in these systems.
Environmental Impact of Geothermal Energy
The environmental impact of geothermal energy depends on its use. Direct use and geothermal heat pumps have a small footprint. But, geothermal power plants emit less than fossil fuel plants.
Geothermal power plants cut acid rain and carbon dioxide emissions by 97% and 99%, respectively. They also recycle water, keeping the resource sustainable for the long term.
In open-loop systems, emissions include carbon dioxide and methane. These systems have emissions of about 0.1 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour. Closed-loop systems, however, do not release these gases.
| Energy Source | Life-Cycle Global Warming Emissions (pounds of CO2 equivalent per kilowatt-hour) |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Geothermal Systems | 0.2 |
| Natural Gas | 0.6 to 2.0 |
| Coal | 1.4 to 3.6 |
By 2050, geothermal energy could be 8.5% of U.S. electricity. It will use only 1.1% of power-sector water. New technology could cut emissions like removing 26 million cars.
Geothermal projects face environmental reviews to ensure responsible development. The U.S. Department of Energy has a plan to manage seismic risks from enhanced geothermal systems.
" Binary-cycle geothermal plants, operating in a closed loop, release essentially zero emissions, making geothermal energy a cleaner alternative to traditional power plants. "
Geothermal Energy in the United States
The United States is a global leader in electricity from geothermal energy. In 2023, seven states produced about 17 billion kilowatt-hours. This is 0.4% of the total U.S. electricity. California is the top producer, making 66.6% of the U.S. geothermal energy.
Leading States in Geothermal Power Production
Nevada is the second-largest producer after California, making 4,296 TWh. Other key states include Utah, Hawaii, Oregon, Idaho, and New Mexico.
The Geysers field in California has 1,517 MW capacity. Nevada's Basin and Range has 19 power plants, with the McGinnis Hills plant being the largest at 96 MW. Hawaii's Puna Geothermal Venture has a 25.7 MWe plant.
" Geothermal generators have a high capacity factor of 92%, making them comparable to nuclear (90%) and higher than gas (87%), or coal (85%). This factor is much higher than those of intermittent sources such as onshore wind (34%) or solar photovoltaic (25%). "
Starting a geothermal field and plant costs about $2500 per kW. Operating and maintenance costs are $0.01 to $0.03 per kWh. This makes geothermal energy a reliable and affordable renewable source in the U.S.
Global Geothermal Energy Production
Geothermal energy is a clean and sustainable power source from the Earth's heat. By 2022, the world's geothermal power capacity hit 16,127 megawatts (MW).
The United States leads in global geothermal energy production, with 3,961.8 MW. Indonesia is second, producing nearly 16 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) in 2021. This is 5% of Indonesia's total electricity.
Other key players include:
- Kenya, where geothermal power makes up 43% of the country's electricity, around 5 billion kWh.
- Australia, which started its first geothermal project in a decade in 2020. It has two small units of 0.155 MW each.
- Chile, which saw a 69% increase in geothermal capacity in the last 3 years. It now has 81 MW in 2022.
Despite growth, there's still a lot of potential. Experts say we could generate up to 210 GW of electricity. This could power about 17% of the world's population.
| Country | Geothermal Power Capacity (MW) | Geothermal Electricity Generation (GWh) | Share of Total Electricity Generation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 3,961.8 | 16,702 | 0.4% |
| Indonesia | 2,561.7 | 15,984 | 5% |
| Turkey | 1,663.0 | 9,413 | 2.7% |
| Philippines | 1,928.4 | 10,463 | 11.8% |
| Mexico | 1,006.4 | 7,136 | 2.2% |
As we move towards cleaner energy, global geothermal energy production is key. It helps meet energy needs and cuts carbon emissions.

Geothermal Energy: Renewable and Sustainable
Geothermal energy is a renewable source because it uses a tiny fraction of the Earth's heat. This heat comes from the Earth's core and will last for billions of years. Geothermal power plants also pollute less than fossil fuel plants, making it a clean energy option.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) says geothermal energy is growing fast. Countries like Turkey, Indonesia, and Kenya are leading the way. Geothermal power plants use wells to tap into hot water or steam deep in the Earth. This steam drives turbines to make electricity.
Geothermal heat pumps are very efficient, using 3 to 6 times less energy than electric boilers. They can cut heating costs by 50% compared to other systems. This makes them a great choice for saving energy and money.
By 2050, geothermal energy could power 65 million homes in the U.S. It could also reduce emissions by taking 20 million cars off the road. The Biden-Harris Administration is investing $31 million to make geothermal energy more affordable and accessible.
| Geothermal Energy: Advantages and Disadvantages |
|---|
|
The Future of Geothermal Energy
The world is moving towards cleaner energy, and geothermal energy is leading the way. Thanks to new technologies and growing interest, the geothermal industry is set for big growth. This change is exciting for the future.
Geothermal Energy Diagram
Geothermal energy uses the Earth's natural heat from its core. It turns this heat into electricity and provides heating and cooling. A detailed diagram helps us understand how it works.
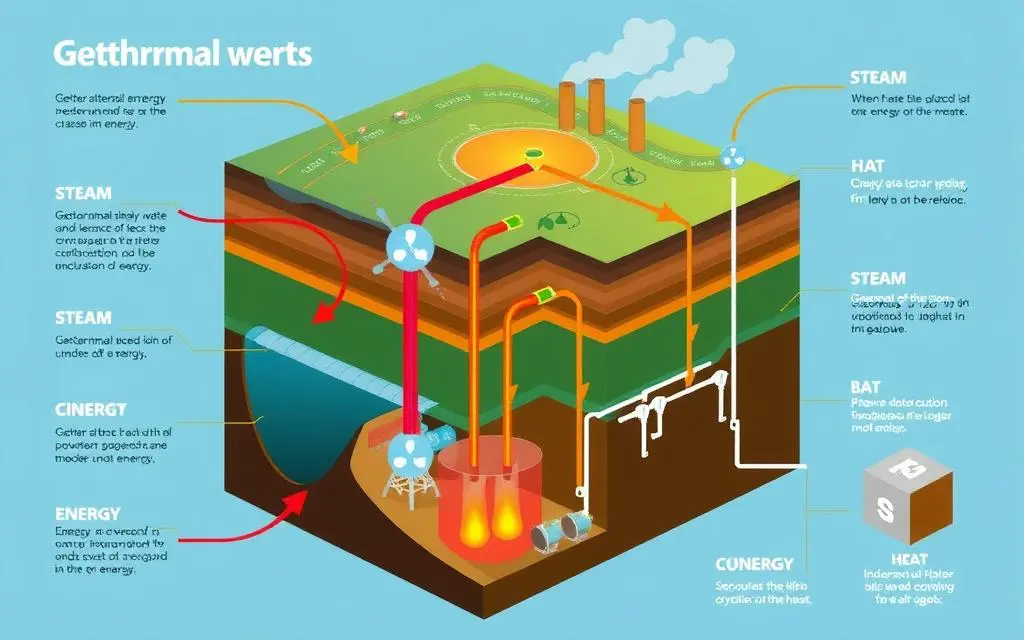
The diagram shows the Earth's core, mantle, and crust. It highlights where the Earth's crust is thin, near tectonic plate boundaries. This is where the heat from inside the Earth is closest to the surface.
Geothermal power plants are built near these areas. They use the heat to generate electricity.
The diagram also shows different types of geothermal power plants. These include dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle plants. Each uses the Earth's heat in a unique way to make electricity or provide heating and cooling.
It also points out direct use applications of geothermal energy. These include district heating systems, greenhouses, and industrial processes. A detailed diagram helps us see how geothermal energy can meet our energy needs in many ways.
" Geothermal energy is a reliable, renewable, and environmentally friendly source of power that can play a significant role in our transition to a sustainable energy future. "
Table of 'Geothermal Energy: Advantages and Disadvantages'
Geothermal energy uses the Earth's heat as a renewable source. It has both good and bad sides to consider. Let's look at the main points about geothermal energy's pros and cons.
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
- Renewable and sustainable resource: Geothermal energy is a renewable source. The Earth's heat is always there, making it a good long-term choice.
- Low emissions: Geothermal power plants make much less carbon dioxide (99% less) and pollutants than fossil fuels.
- Consistent power generation: Geothermal plants can run at high capacity, often over 80%. This makes electricity reliable and steady.
- Versatile applications: Geothermal energy can be used for electricity and heating/cooling. It has many uses.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: Using geothermal energy means less need for fossil fuels. This helps with energy independence and security.
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
- High upfront costs: Starting a geothermal project can be very expensive. Costs can be from $2 to $7 million per megawatt.
- Limited geographical availability: Geothermal resources need special geological conditions. This limits where it can be used.
- Potential environmental impacts: Geothermal operations can harm local water if not done right. There's also a risk of causing earthquakes.
- Reservoir depletion: If too much fluid is taken out, geothermal reservoirs can run dry. It's important to manage this carefully.
In summary, geothermal energy's benefits like being renewable, low emissions, and steady power must be balanced with its drawbacks. These include high costs, limited use areas, and environmental risks. With careful planning and sustainable practices, we can make the most of this valuable energy source.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is a clean and sustainable power source. It uses the Earth's natural heat. This energy can power homes, businesses, and industries.
The Earth's core is incredibly hot, reaching up to 10,800 degrees Fahrenheit. This heat comes from radioactive decay and pressure in the Earth's mantle. By tapping into this heat, especially near tectonic plate boundaries, we can use more geothermal energy.
In the United States, most geothermal power plants are in western states and Hawaii. California leads, producing 69.5% of the country's geothermal electricity. In 2021, these plants made about 0.4% of the U.S. electricity.
Geothermal energy is valuable worldwide, not just in the U.S. In 2021, 28 countries, including the U.S., made about 92 billion kWh of electricity from geothermal sources. Indonesia and Kenya are among the top producers, showing its global importance.
Geothermal energy is not just for electricity. It's also used for heating and cooling. Geothermal heat pumps use the Earth's constant temperature to efficiently heat and cool buildings.
As we look for clean energy, geothermal stands out. It's reliable and can meet our energy needs. With new technology and more investment, geothermal will be key in our sustainable future.
" Geothermal energy is a renewable, sustainable, and clean energy source that can play a crucial role in meeting the world's growing energy needs while reducing our carbon footprint. "
Conclusion
Geothermal energy is a promising renewable source with great potential for a sustainable future. It offers reliable power, low environmental impact, and exciting tech advancements. This makes it a key player in reducing our dependence on fossil fuels.
The United States leads in geothermal energy production. It's ready to unlock this natural resource's full potential. With new tech, policies, and research, the industry could grow. This could meet over 8% of the country's electricity needs by 2050.
As the world's energy needs change, geothermal's role grows. It's key to a cleaner, greener future. By using the Earth's power, we can cut emissions, protect the environment, and ensure energy for future generations.
FAQ
What is geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy comes from the earth's heat. It's called geo (earth) + thermal (heat). This energy is found in hot water reservoirs under the earth. It's used for electricity, heating, cooling, and more.
How long has geothermal energy been used?
People have used geothermal energy for bathing since ancient times. They used it for heating since the Roman era. The first industrial use was in 1827 in Italy. The world's first commercial plant was built there in 1911.
Where are geothermal resources most abundant?
Geothermal resources are found near tectonic plate boundaries. These areas have thinner crusts and more heat, like the "Ring of Fire" around the Pacific.
What are the main types of geothermal power plants?
There are three main types of geothermal power plants. Dry steam plants use steam directly from the earth. Flash steam plants convert high-pressure hot water to steam. Binary cycle plants use another liquid to turn to steam.
How is geothermal energy used for heating and cooling?
Geothermal heat pumps use the earth's stable temperature to heat and cool buildings. They move heat from the ground into buildings in winter and out in summer.
What are the environmental benefits of geothermal energy?
Geothermal power plants have low emissions. They release much less acid rain-causing sulfur compounds and carbon dioxide than fossil fuels. They also recycle water, helping to keep the geothermal resource.
Which US states are leading in geothermal power production?
California leads in geothermal power, making up 69.5% of U.S. production. Nevada, Utah, Hawaii, Oregon, Idaho, and New Mexico are also top producers.
How much of the world's electricity is generated from geothermal energy?
By 2021, 27 countries produced about 92 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity from geothermal energy. Indonesia was the second-largest producer, making nearly 16 billion kWh, or 5% of its total electricity.
Is geothermal energy considered a renewable resource?
Yes, geothermal energy is renewable. The heat extraction rates are very small compared to the earth's heat. The earth's heat will keep being replenished for billions of years.
What is the future potential for geothermal energy?
Studies show the U.S. could have up to 90 GW of geothermal capacity by 2050. With new technologies, this could reach 300 GW. This growth could help the nation switch to clean energy.
" This page contains affiliate links. If you purchase through these links, I may earn a commission at no additional cost to you. As an affiliate for Amazon and other companies, I earn from qualifying purchases. "